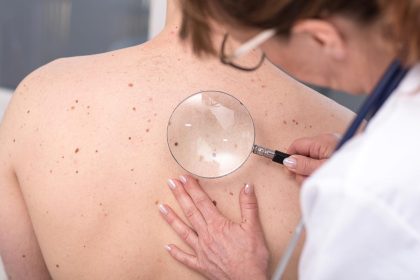
Basal cell skin cancer is a type of skin cancer that occurs as a result of the uncontrolled growth of basal cells in the top layer of the skin (epidermis). Basal cell skin cancer is one of the most common type of cancers in the body and occurs mostly in sun-exposed areas such as face, ears, neck, hands, and arms.
Basal cell skin cancer is usually a slow-growing type of cancer and often does not spread, but it can become larger and more widespread if left untreated. Basal cell skin cancer can usually be successfully treated if diagnosed early.
Factors Causing Basal Cell Skin Cancer
The exact cause of basal cell skin cancer is not known. However, factors such as exposure to sunlight, light skin color, older age, skin burns, radiation exposure, immunosuppression, and familial predisposition are considered to be influential.
Exposure to sunlight is a major risk factor as UV rays damage the DNA of the skin and cause the uncontrolled growth of skin cells. Also, having a fair complexion causes the skin to become more sensitive to UV rays due to less melanin pigment.
Aging also increases the risk of basal cell skin cancer because skin cells become more susceptible to damage with age. Skin burns and radiation exposure can also increase the risk of basal cell skin cancer.
Immune suppression makes cancer cells vulnerable to cancer cell growth, while familial predisposition can also increase the risk of basal cell skin cancer. People with a family history of skin cancer may have a higher risk of basal cell skin cancer.
Basal Cell Skin Cancer Treatment
The treatment of basal cell skin cancer may vary depending on the type, size, location, spread of the cancer, and the patient’s general health condition. Usually, treatment options such as surgery, radiotherapy, cryotherapy (freezing), and topical medications are used.
Surgical intervention; It is an operation to remove cancerous tissue. For small cancers, it can be performed under local anesthesia and surgical removal. For larger cancers, it may be done under general anesthesia and the surgical area may need to be closed with skin grafts (patches) or flaps.
Radiotherapy; It means using high energy radiation to kill cancer cells. It can be applied as local radiotherapy by directly targeting cancer cells.
Cryotherapy; It is a method used to freeze cancerous tissue. By applying liquid nitrogen or another cooling agent to the cancerous area, the cancerous cells are frozen and killed.
Topical medications; It is another method used for the treatment. Applied as a cream or lotion, these drugs are used to kill cancerous cells or stop their growth. These drugs are usually suitable for small and superficial cancers.
The treatment option depends on the type and severity extent of the patient’s cancer. Early diagnosis and treatment of cancer can lead to successful results. Therefore, it is important to have regular skin checks and to protect the skin when exposed to the sun.
Please click for contact information.







You must be logged in to post a comment.