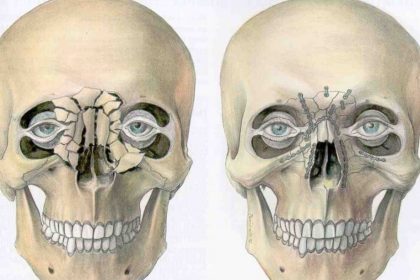
What are Facial (Maxillary, Zygomatic, Orbital) Fractures?
Facial fractures include fractures and depression of the bones which form the facial structure. These fractures could result from various accidents such as home injuries, occupational accidents or traffic accidents. In some conditions, the facial skin could remain intact, but more commonly, damage to the facial skin accompanies the fracture. Facial fractures are hard to diagnose in the early period since swelling and edema of the subcutaneous tissue might conceal the pathology. In such cases, underlying deformities appear when edema decreases a few days after the trauma.
What do the Facial Fractures Include?
- Nasal fracture
- Jaw fracture
- Orbital (eye socket) fracture
- Midface fracture
How is the Treatment Method Determined in Facial Fractures?
Fractures are diagnosed by detailed scanning with various radiological methods (such as computed tomography). Reduction of the fracture and fixation by using plates-screws or wires are performed. Other traumatic injuries usually accompany facial fractures. Concurrent head trauma should be investigated. The presence of any other injuries such as abdominal and extremity injuries should be checked. In case of loss of consciousness during the accident or in case of nausea-vomiting neurosurgeon’ s examination is required.
Which Procedures are Applied in Facial Fracture Surgeries?
Facial fracture procedures are usually performed under general anaesthesia. Small incisions are made to reach the fracture site. Either the oral cavity or the facial skin is incised depending on the fracture type. Skin incisions are usually made on skin curves, hair border, lower eyelid rims. In need of bone or tissue transplants, an additional incision is made. After the anatomic reduction and realignment of the fracture, fixation is performed by using one or more of the following materials:
- Titanium plate and/or screws
- Biodegradable plate and/or screws
- Wire braces
- Dental metal arc and wires
- External fixators (which are externally applied tools)
- Autologous bone grafts
- Cadaveric bone, cartilage, bone cement, Orthobone powder
- Alloplastic materials such as silicone, microcrystalline, hydroxyapatite complex, methyl methacrylate, titanium mesh
These materials can remain life-long unless they disturb the patient. If a disturbance occurs, a second surgery would be performed to remove these implants.
Facial Fractures Frequently Asked Questions
Consultant Plastic, Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgeon Professor Yazar is available in his private practice based in Nisantasi, Istanbul for appointments to provide detailed and tailored information on the procedure.






You must be logged in to post a comment.